Introduction
RAG stands for Retrieval-Augmented Generation. It is a technique that enhances Large Language Models (LLMs) by providing them with external (proprietary) information to increase their accuracy and responsiveness. In other words, RAG allows you to combine your own data with an LLM. Instead of sending questions directly to the LLM, it supplements them with relevant information from your sources, enabling it to generate better, contextualized answers based on your data.
To do this, RAGs typically use vector databases, which are specialized for storing and querying vector embeddings. Documents are usually split into chunks, and their embeddings are calculated. These embeddings are used to represent information in a vector space, allowing for similarity-based queries and efficient retrieval of meaningful information.
On the other hand, a knowledge graph is a way of representing information in a structured manner, using nodes to represent entities and relationships to connect them, showing how they relate to each other. This structure, similar to a concept map, allows for capturing the depth and contextuality of information in a way that traditional vector databases, which rely on unstructured data, often cannot.
To learn a bit about building RAGs and how knowledge graphs can be used to improve them, we will conduct some tests using LangChain as the LLM development framework and Neo4j as the graph database.
Building the Knowledge Graph
To build a knowledge graph, we first need to define the entities and relationships we want to represent. In our case, we are going to build a knowledge graph that represents information about the most effective study techniques and how they relate to each other.
For this, we will use the Neo4j graph database and its visual tool, Graph Builder, to construct the knowledge graph.
This tool is capable of using AI to extract nodes and relationships from the documents you provide and build a knowledge graph with them.
We simply provided it with the Wikipedia page on Study Skills and, with a little help (by providing the entities we wanted to extract for our tests), it built the following knowledge graph for us:
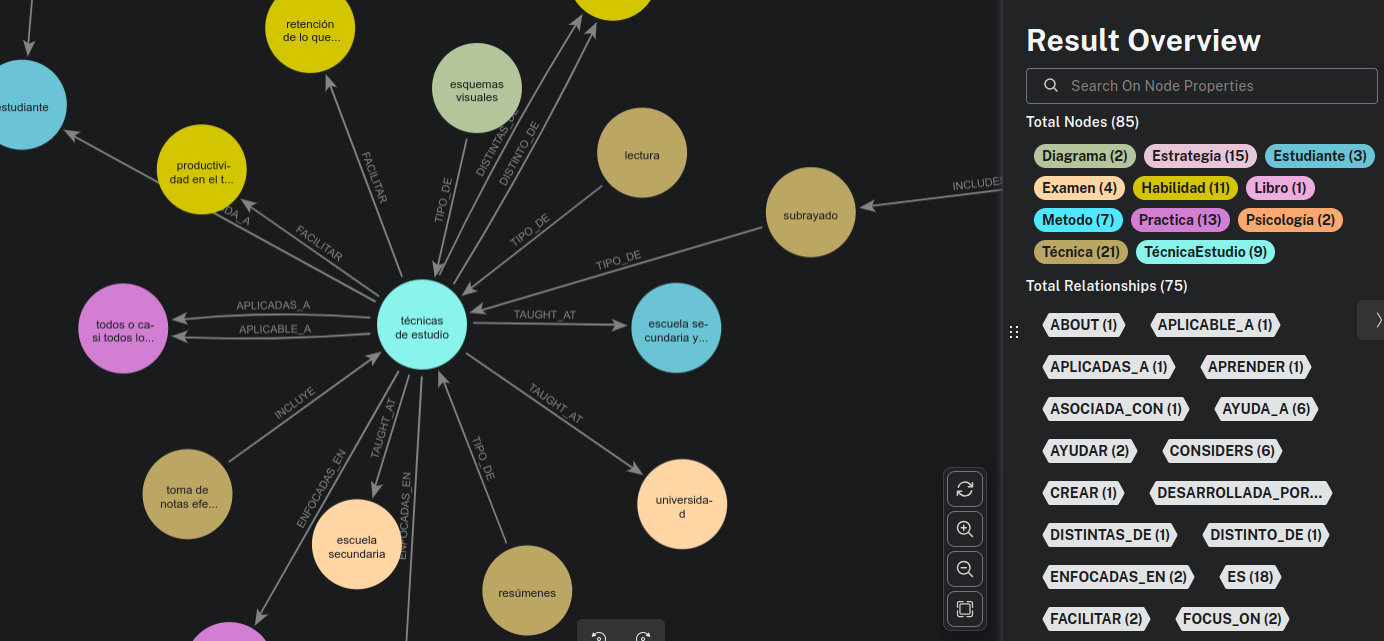
As we can see, the graph outlines, among other things, the different study techniques that can be used and how they relate to each other: underlining, summarizing, creating outlines, planning the learning process, reviewing, etc.
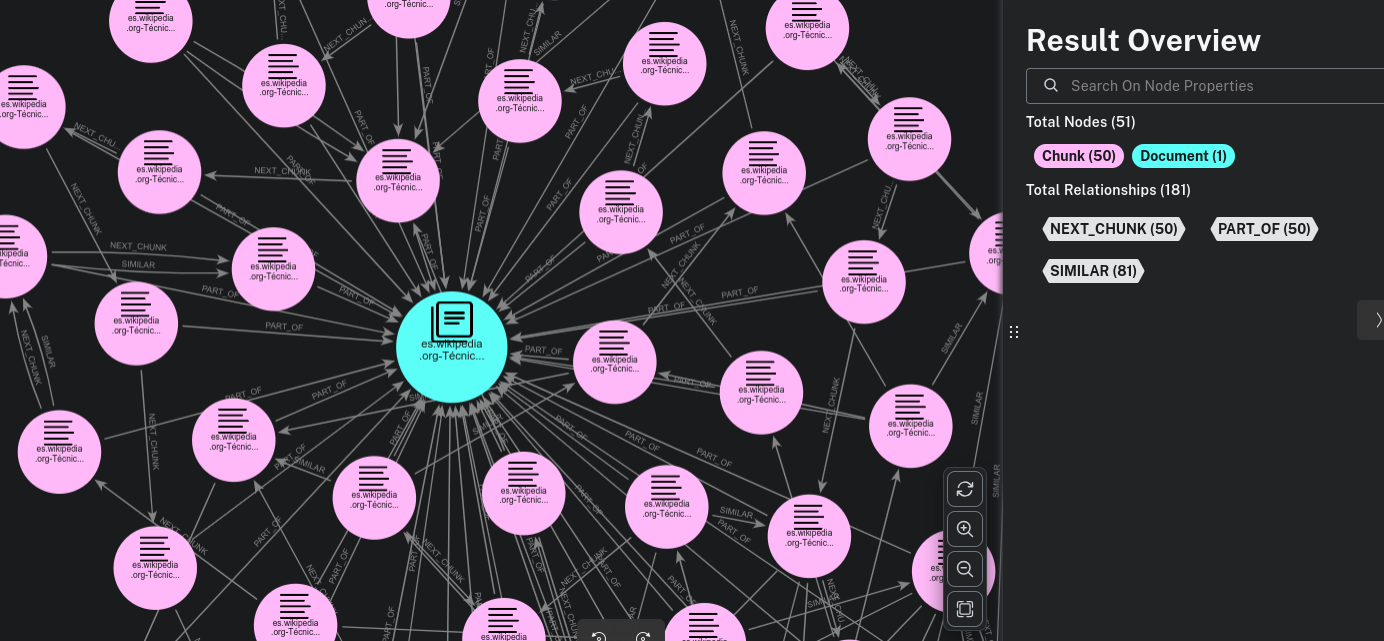
The great thing about Neo4j databases is that they also act as vector databases. In the same process, the Graph Builder has split the document into chunks and calculated their embeddings to allow for similarity-based queries. This is stored in another graph (connected to the previous one), which can be seen in the following image:
Accessing the Knowledge Graph from LangChain
Once we have built our knowledge graph in Neo4j, we connect to it using LangChain.


